Future in Focus: Unveiling Potential with Infrared Sensor Technologies| Types and Applications
Infrared sensor technologies revolve around detecting infrared radiation, reaching beyond the limits of the visible light spectrum. This distinctive capability unfolds numerous possibilities, offering a diverse range of applications across different industries.

The adaptability of Infrared Sensor Technologies has resulted in their extensive integration across various sectors, spanning security, automotive, and healthcare. Grasping the importance of Infrared Sensor Technologies is vital to truly comprehend the impact they wield on contemporary lifestyles.
Varieties of Infrared Sensors Technologies
Infrared Sensor Technologies are available in diverse types, each tailored to specific requirements:
Passive Infrared (PIR) Sensors:
Security Systems
Within security setups, PIR sensors activate when an individual moves within their field of view. The distinct temperature change caused by body heat triggers the sensor, initiating an alarm and augmenting the effectiveness of the security system.
Automatic Lighting
PIR sensors play a crucial role in energy-efficient automatic lighting systems. Upon detecting someone entering an area under PIR sensor surveillance, the temperature change activates the lights, providing both energy savings and convenience by illuminating precisely when needed.
Conservation Initiatives
In the conservation domain, PIR sensors contribute to monitoring wildlife movement in protected areas. This aids researchers in tracking populations and protecting ecosystems from potential disturbances.

PIR Working
- Internal Components: Within the PIR sensor, two pyroelectric crystals generate a small voltage in response to infrared radiation.
- Maintaining Thermal Equilibrium: Under stable ambient temperatures, the voltages from both crystals within the sensor offset each other, maintaining thermal equilibrium.
- Identifying Warm Objects: When a warm object, such as a person, enters the sensor’s field, it disrupts thermal equilibrium. This disruption results in an elevation in voltage from one crystal and a corresponding reduction from the other.
- Electronic Response: The voltage difference triggers the sensor’s electronics, initiating a signal that signifies the detection of movement.
Limitations of PIR Sensors:
- Undiscriminating Heat Detection: PIR sensors lack the capability to distinguish between different heat sources, posing the risk of potential false alarms triggered by pets or other warm objects.
- Blind Spots: The presence of blind spots in PIR sensors is contingent on their placement and detection angle, constraining their coverage in specific scenarios.
- Environmental Factors: External elements such as drafts or sudden temperature changes can contribute to false alarms with PIR sensors, emphasizing the need for meticulous consideration during the installation process.
2. Active Infrared (AIR) Sensor
Active Infrared (AIR) sensors function as the Sherlock Holmes of the invisible domain, employing infrared radiation to unveil secrets concealed from our unaided vision. Unlike their passive counterparts, such as PIR sensors that only register changes in existing infrared, AIR sensors adopt an active approach by emitting their own infrared beam. They meticulously measure the reflection of this beam to extract crucial details about distance, size, and even material composition.
AIR sensor Working
Picture a spotlight, but instead of visible light, AIR sensors emit a concentrated beam of infrared radiation. As this beam interacts with an object, its characteristics undergo slight changes. Through meticulous analysis of the reflected beam, AIR sensors can determine:
- Distance: AIR sensors precisely ascertain the distance to an object by calculating the time it takes for the emitted beam to travel to and from the target. This accuracy proves essential for various applications, including laser rangefinders utilized in surveying, robotics, and autonomous vehicles. Additionally, it plays a critical role in collision avoidance systems integrated into cars and drones.
- Object Identification: Some AIR sensors go beyond distance measurement. By scrutinizing the intensity and phase shift of the reflected beam, they can differentiate between various materials, shapes, and sizes. This capability finds applications in object classification, security systems, and traffic monitoring.
Limitations of AIR Sensors:
- Cost: The inclusion of additional components such as lasers and complex signal processing circuitry makes AIR sensors considerably more expensive than their passive counterparts, PIR sensors.
- Line-of-Sight Requirement: Unlike PIR sensors, which can partially “see” around corners, AIR sensors necessitate an unobstructed path to the object, limiting their effectiveness in cluttered environments.
- Power Consumption:
The active radiation emission by AIR sensors accelerates battery depletion compared to passive detection, reducing their suitability for battery-powered applications. - Environmental Factors:
Adverse weather conditions like heavy rain, snow, or fog can undermine the effectiveness of the infrared beam emitted by AIR sensors, affecting both its range and accuracy. - Safety Concerns:
High-powered AIR sensors carry the potential to emit radiation at levels that may be harmful, necessitating the implementation of proper safety measures and the use of eye protection. - Security Vulnerabilities:
The emitted beam from AIR sensors is susceptible to interference through jamming or spoofing, introducing the risk of inaccurate measurements and potential security breaches. - Complexity:
In comparison to PIR sensors, AIR sensors display a higher level of complexity, resulting in increased maintenance requirements and potential challenges in troubleshooting.
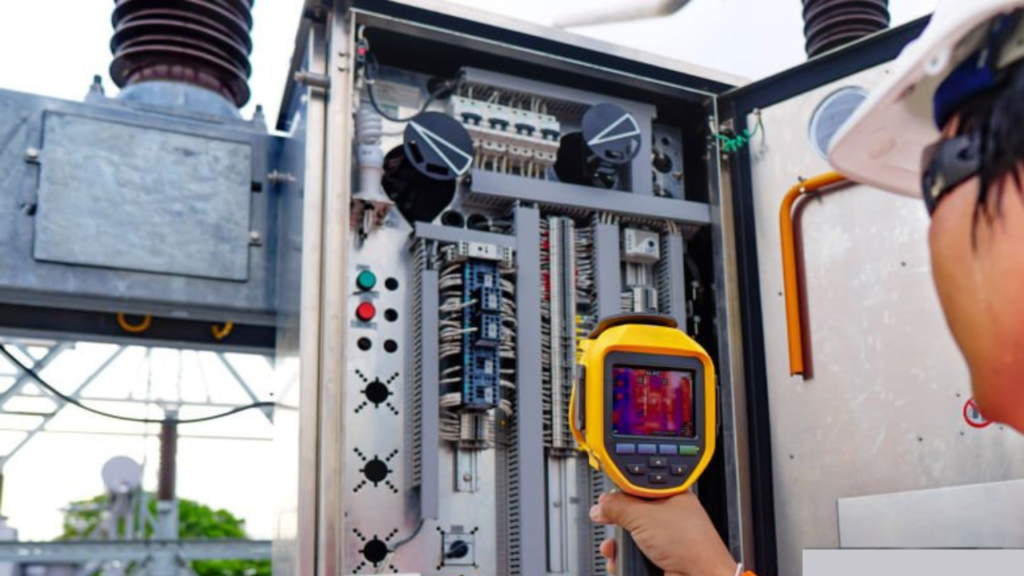
3. Thermal Imaging Sensors
Thermal Imaging Sensors function by creating detailed images that capture temperature variations, making them exceptionally suitable for diverse applications in the medical and environmental sectors.
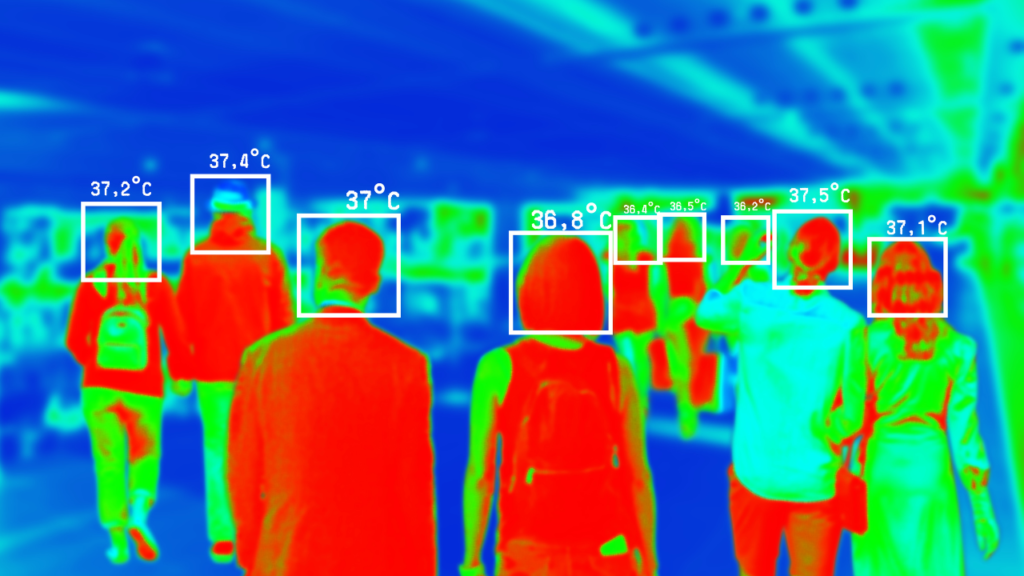
Thermal Imaging Sensors Working
- Mapping Temperature Variations: These sensors excel in mapping temperature differences across surfaces, generating visual representations that highlight temperature gradients by detecting variations in thermal energy.
- Medical Applications: Within the medical domain, Thermal Imaging Sensors assume a crucial role. They facilitate the non-invasive detection of abnormalities in body temperature, assisting in the early diagnosis of conditions such as inflammation or circulation disorders. Furthermore, these sensors are utilized in thermal imaging cameras for fever screening and monitoring the health of patient.
- Environmental Monitoring: Thermal Imaging Sensors play a vital role in environmental studies, offering valuable insights into temperature patterns within ecosystems. Researchers utilize them to evaluate the impact of climate change, monitor wildlife movement, and identify regions experiencing unusual temperature fluctuation.
- Building Inspections: Deployed in building inspections, these sensors unveil temperature variations indicating structural issues, electrical problems, or insulation deficiencies. This aids in preventive maintenance and enhances energy efficiency.
- Search and Rescue Operations: Thermal Imaging Sensors are essential in search and rescue missions, detecting heat signatures. In situations like natural disasters or locating missing persons, these sensors enhance visibility, significantly increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Limitations:
- Cost: High-quality Thermal Imaging Sensors can be relatively expensive, impacting accessibility for certain applications.
- Resolution Constraints: Some sensors may have limitations in resolution, affecting the level of detail in captured thermal images.


