What nuclear medicine technologist do? Future Scope & Career:
Nuclear Medicine Technology
Nuclear Medicine Technology is a dynamic and vital discipline within the realm of healthcare that combines advanced technology with patient care. This field revolves around the use of radioactive materials to diagnose and treat various medical conditions, providing invaluable insights into the functioning of organs and tissues at a molecular level.
Nuclear medicine technologists, the skilled professionals in this field, play a pivotal role in the diagnostic process. They work closely with a diverse healthcare team, utilizing specialized equipment to administer and monitor radioactive drugs. These professionals are adept at capturing detailed images that aid physicians in making accurate diagnoses and developing effective treatment plans.

The scope of Nuclear Medicine Technology extends beyond imaging. Technologists are involved in analyzing specimens in the laboratory, ensuring precision in diagnostic procedures. Their responsibilities also include limiting radiation exposure to patients and staff, highlighting the crucial emphasis on safety.
Nuclear Medicine Technologist
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, nuclear medicine technology stands out as a cutting-edge field that plays a crucial role in diagnosis and treatment. Nuclear medicine technologists perform tests for diagnosis and medical research. They prepare and give small doses of radioactive drugs (radiopharmaceuticals) to patients, then use high-level imaging equipment to record images of the radioactive material in the body. Physicians interpret the images to study and diagnose an infection or disorder. Nuclear medicine technologists also give doses of radiation to patients internally to treat medical conditions.
Educational Requirements for Becoming a Nuclear Medicine Technologist
To pursue a profession as a nuclear medicine technologist, individuals need to fulfill precise educational prerequisites. In this section, we delve into the comprehensive academic journey, outlining the specific degrees and certifications that are fundamental for entering the field of nuclear medicine technology.
Higher education requirements
While the pathway to becoming a nuclear medicine technologist may look different for each individual, most employers require the following:
- Completion of an associate degree or bachelor’s degree
- Completion of a certificate program that specializes in nuclear medicine technology
In most circumstances, the difference between having an associate degree or a bachelor’s degree will determine which professional certifications for which you can apply and there may be some difference in on-the-job responsibilities.
Certification process
Many employers require certification or licensure to work as a nuclear medicine technologist. Certification is available for individuals who have completed a nuclear medicine program and passed the certifying exam from a certification board like the Nuclear Medicine Technology Certification Board or the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists.
Scope of Responsibilities
The role of nuclear medicine technologists involves collaboration with a multidisciplinary team, including doctors, medical physicists, nuclear pharmacists, computer specialists, nurses, and administrative staff.
Key tasks and responsibilities associated with the position encompass:
-
Preparing and Administering Radioactive Drugs:
Nuclear medicine technologists are responsible for the accurate preparation and administration of radioactive drugs, a crucial step in the diagnostic process.
-
Capturing Diagnostic Images:
These professionals capture images using specialized equipment, providing physicians with essential visuals for diagnosing infections or disorders.
-
Limiting Radiation Exposure:
Ensuring the safety of both patients and staff, nuclear medicine technologists implement measures to minimize radiation exposure during diagnostic procedures.
-
Analyzing Specimens in the Lab:
Beyond imaging, technologists play a role in analyzing specimens in the laboratory, contributing to the overall diagnostic process.
-
Setting Up Appointments:
Nuclear medicine technologists are involved in the logistics of scheduling appointments, ensuring a smooth and efficient process for patients.
-
Explaining Procedures to Patients:
A crucial aspect of the role is providing clear and comprehensive explanations of procedures to patients, offering support and information throughout the diagnostic experience.

Importance of Nuclear Medicine in Diagnostics
Nuclear medicine plays a pivotal role in diagnostic imaging, providing insights into the functioning of organs and tissues. Learn about the significance of nuclear medicine in diagnosing and treating various medical conditions.
Advancements in Nuclear Medicine Technology
Technological advancements continuously reshape the landscape of nuclear medicine. This section explores the latest innovations and how they contribute to improving accuracy and patient outcomes.
Career Opportunities for Nuclear Medicine Technologists
The need for nuclear medicine technologists is experiencing a notable increase. Explore the expansive array of career prospects awaiting individuals in this field, ranging from employment opportunities in hospitals and clinics to roles within research institutions and various other healthcare settings.
Diverse Paths, Rewarding Journeys
Nuclear medicine technologists hold a unique position in healthcare, wielding radioactive tracers and specialized imaging to illuminate internal processes and guide diagnoses. But their skills and knowledge translate to a surprisingly diverse range of career paths, offering exciting options for those passionate about this field. Here’s a glimpse into the spectrum of opportunities awaiting:
1. Clinical Settings:
- Hospital nuclear medicine departments: The traditional setting, where technologists perform a wide range of nuclear medicine procedures for diagnosis and treatment planning (e.g., bone scans, thyroid scans, cardiac PET scans).
- Outpatient imaging centers: Offering convenient access to nuclear medicine services for a broader patient population.
- Oncology clinics: Working closely with cancer specialists to support diagnosis, staging, and treatment monitoring of tumors.
- Cardiology clinics: Providing specialized heart scans to assess blood flow and function, aiding in the diagnosis and management of heart disease.
- Research institutions: Contributing to clinical trials and research studies, testing new radiopharmaceuticals and imaging techniques.
2. Beyond Clinical Environments:
- Radiopharmaceutical companies: Collaborating in the development and production of safe and effective radiopharmaceuticals.
- Nuclear medicine equipment manufacturers: Contributing to the design, testing, and improvement of imaging equipment.
- Educational institutions: Teaching future generations of nuclear medicine technologists, sharing their expertise and passion for the field.
- Regulatory agencies: Ensuring the safe and ethical use of radioactive materials in nuclear medicine practices.
- Consulting firms: Applying their knowledge and experience to advise hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare organizations on nuclear medicine practices and procedures.
3. Specialized Expertise:
- PET/CT technologists: Mastering the skills needed to operate and interpret combined PET (positron emission tomography) and CT (computed tomography) scans, offering detailed anatomic and functional information.
- Nuclear cardiology technologists: Specializing in cardiac imaging procedures, providing crucial information for diagnosing and managing heart conditions.
- Thyroid specialists: Focusing on diagnosing and monitoring thyroid disorders using specialized nuclear medicine techniques.
- Research technologists: Advancing the field through involvement in cutting-edge research projects and development of new technologies.

What nuclear medicine technologist do? Future Scope & Career
Salary and Compensation in the Field
Understanding Compensation in the Nuclear Medicine Technology Profession Recognizing the significance of compensation in any occupation, it’s imperative to delve into the intricate details of the salary structure for nuclear medicine technologists. This involves gaining insights into the various factors that influence their earnings, including experience, specialization, geographical location, and the specific healthcare setting in which they practice. By exploring these elements, individuals can obtain a comprehensive understanding of the financial landscape within the field of nuclear medicine technology.
Challenges and Rewards in the Profession
Explore the intricacies of the nuclear medicine technologist profession, uncovering a spectrum of challenges and rewards inherent to this unique career. Navigate through the complexities, ranging from tackling technological hurdles that arise in the dynamic field to savoring the gratification derived from actively contributing to the well-being and care of patients. Delve into the nuanced experiences that make the journey of a nuclear medicine technologist distinctive, encompassing both the demanding aspects and the deeply rewarding moments tied to patient care and diagnostic precision.
Impact of Nuclear Medicine on Patient Care
Investigate the profound influence of nuclear medicine on enhancing patient care through the facilitation of early and precise diagnoses. This, in turn, not only expedites the commencement of medical interventions but also contributes significantly to the formulation and execution of more efficacious treatment plans for individuals undergoing medical evaluation and care.
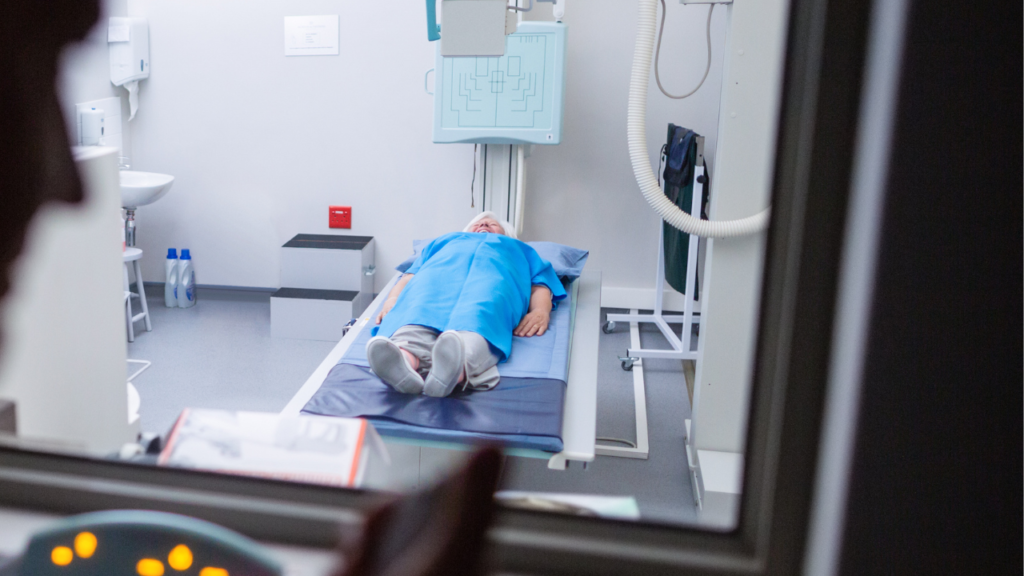
Future Trends in Nuclear Medicine Technology
The realm of nuclear medicine is characterized by its dynamic nature, constantly evolving with continuous developments. This section invites you to explore and gain insights into the emerging trends that are anticipated to mold the trajectory of the profession in the foreseeable future, examining their potential impact on the broader landscape of healthcare.
Key Skills Required for Success
Achieving success in the field of nuclear medicine technology demands a well-defined and specialized set of skills. Let’s delve into the critical attributes essential for a prosperous career, encompassing not only technical proficiency but also strong communication and problem-solving abilities. These skills collectively form the foundation for excellence in the dynamic and demanding field of nuclear medicine technology.

